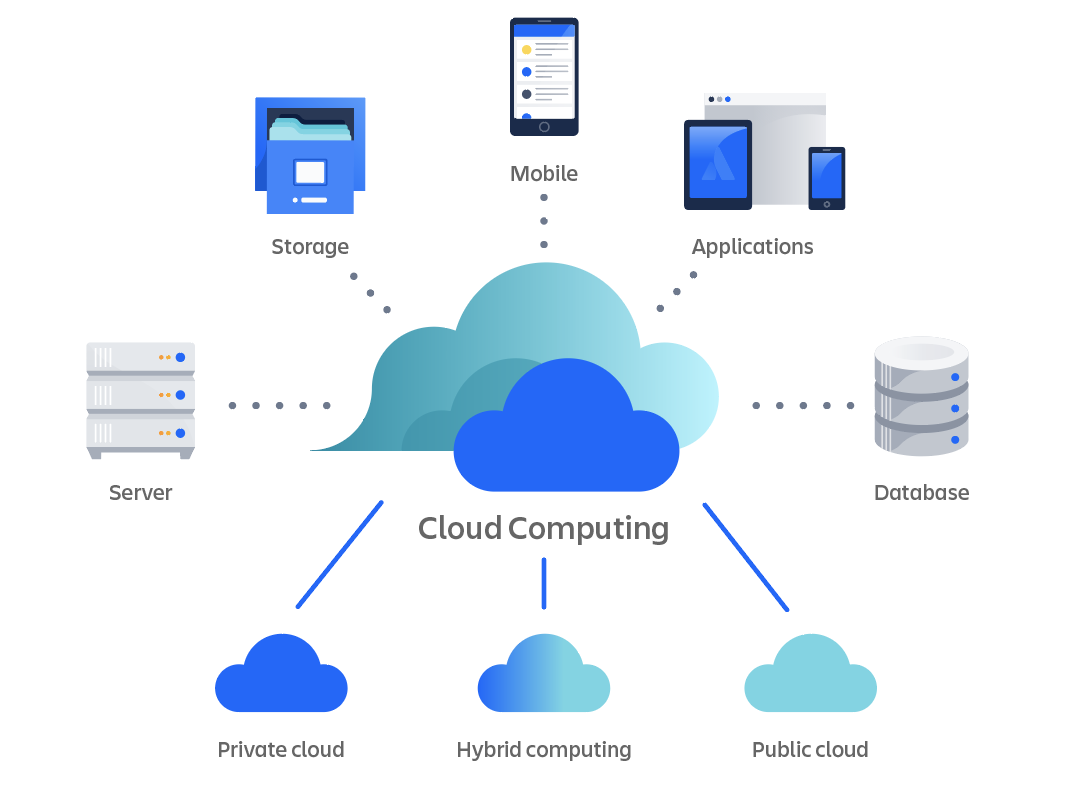
As cloud computing matures commercially and technologically, companies are taking advantage of its many benefits. Familiarizing yourself with the essential cloud computing characteristics can help you maximize those benefits to grow and strengthen your business.
Characteristics
- Upon Request Self-Service
You may automatically provision computer resources, such as server time and network storage, with cloud computing. There is no need for you to communicate with the service provider. Customers of cloud services can view their cloud services, track their usage, and provision and de-provision services by logging into their cloud accounts through a web self-service portal.
- Pooling Of Resources
Using a multi-tenant approach, resource pooling enables numerous customers to share physical resources. Based on demand, this model distributes and redistributes real and virtual resources. Customers can share the same applications or infrastructure with multi-tenancy while still retaining their privacy and security.
Customers may be able to designate the location of their resources at a higher level of abstraction, such as a country, state, or data center, even though they won’t know the precise location of their resources. Customers can pool a variety of resources, including memory, computing power, and bandwidth.
- Determined Service
A metering capability in cloud systems optimizes resource utilization at an abstraction level appropriate for the type of service. For storage, processing, bandwidth, and users, for instance, you can utilize a measured service. A pay-for-what-you-use model is used to base payments on the customer’s actual consumption. Consumers and service providers benefit from a transparent experience that is created by monitoring, managing, and reporting resource use.
- Extensive Network Access
Resources for cloud computing are accessible via the internet and can be accessed by a variety of customer platforms. In other words, cloud services can be accessed through a network—ideally a high-speed Internet connection—or, in the case of private clouds, a local area network (LAN).
Given that they are related to the quality of service (QoS) on the network, network bandwidth and latency are crucial components of cloud computing and widespread network access. For supporting time-sensitive manufacturing applications, this is especially crucial.
- Virtualization
To isolate underlying hardware resources and display them to consumers as logical resources, cloud computing companies use virtualization technology.
- Computing That Is Resilient
Redundancy and fault tolerance are frequently taken into consideration while designing cloud computing services, ensuring high availability and dependability.
- Flexible Pricing Structures
Cloud service providers provide a range of price structures, including pay-per-use, subscription-based, and spot pricing. Users can select the model that best meets their requirements.
Conclusion
Here, we’ve quickly covered a variety of cloud computing properties. Cloud computing is more affordable, more secure, automated, mobile, accessible, adaptable, resilient, and scalable.
FAQ
1. What is cloud computing, and what are its features?
In essence, cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of computing resources, such as storage, applications, networking capabilities, databases, software and services, development tools, processing capabilities, and more, to users via the internet by service providers (also referred to as Cloud Service Providers or CSP).
2. What qualities does cloud computing on-demand self-service have?
While mobile computing focuses on device mobility and context awareness while taking networking and mobile resource/data access into consideration, cloud computing focuses on on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service.
3. What is cloud computing, and what are its features?
J. C. R. Licklider is credited with creating cloud computing in the 1960s with his work on the ARPANET, which connected people and data at any time, any place.
4. What feature of cloud computing restricts access?
In order to prevent conflicts, it restricts access to each application to a single user at a time. It allocates specific clients a share of its computing resources. It permits the sharing of applications across numerous users while protecting data privacy.